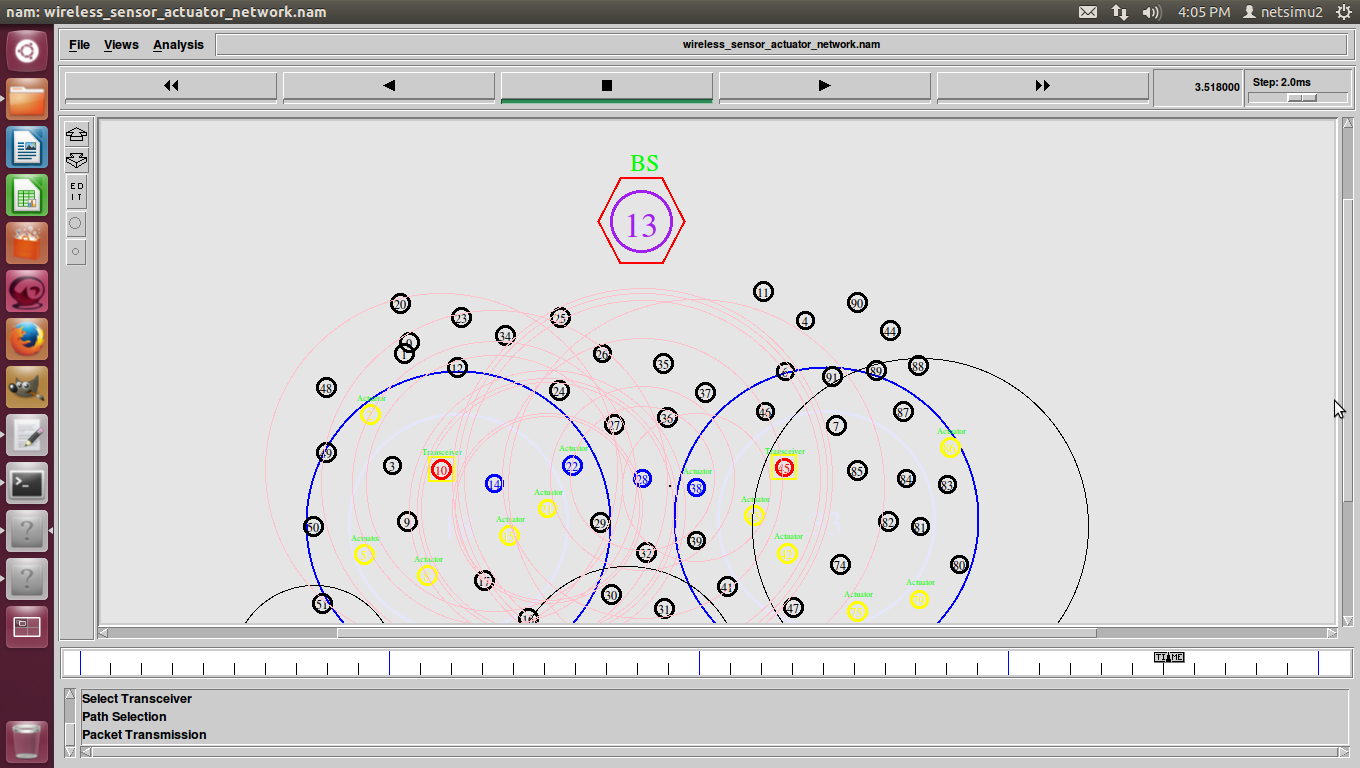
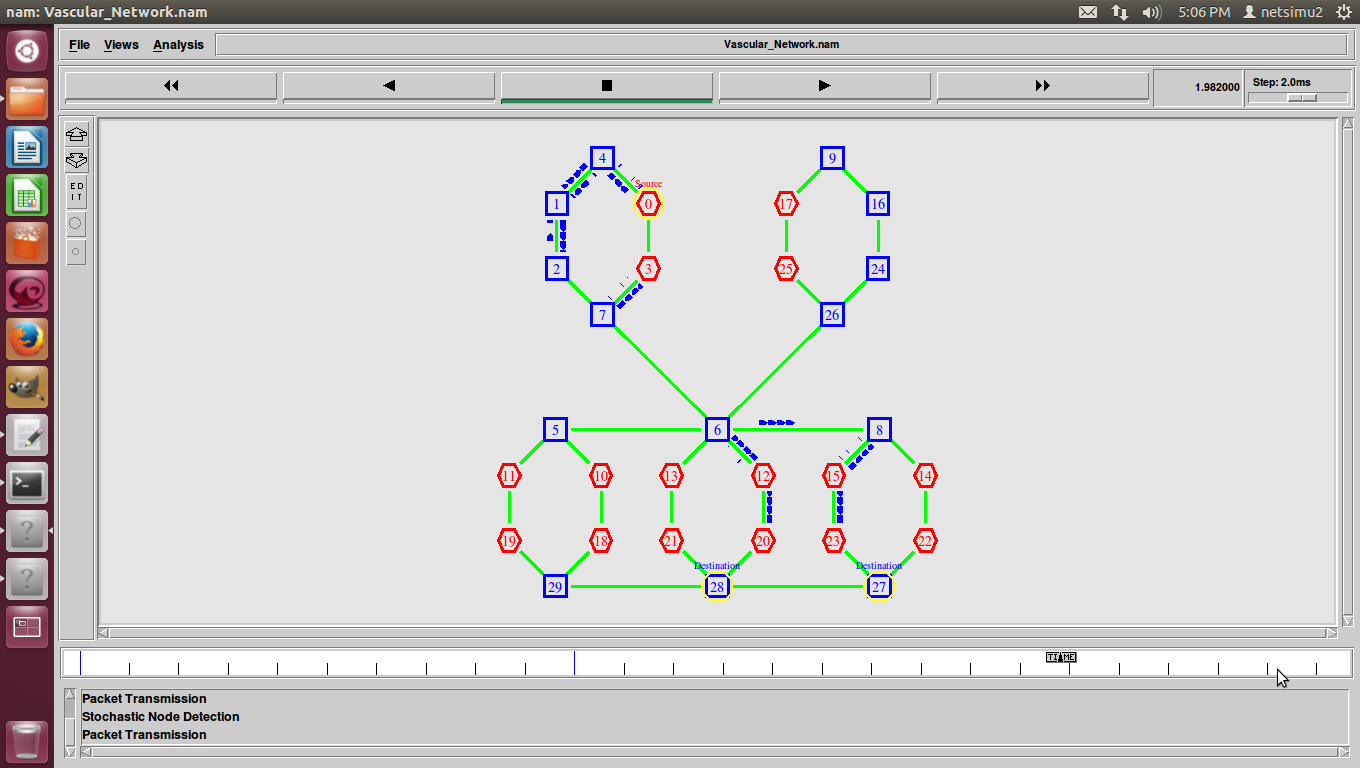
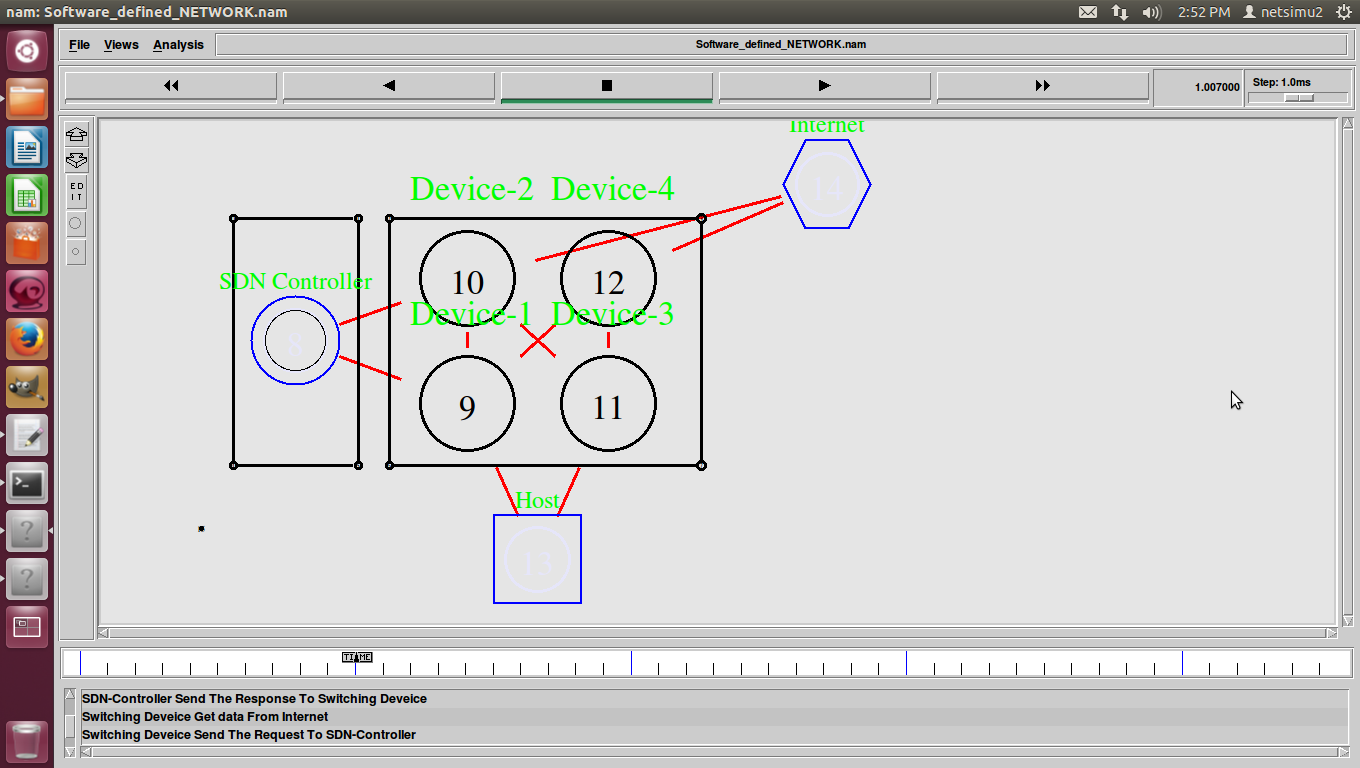
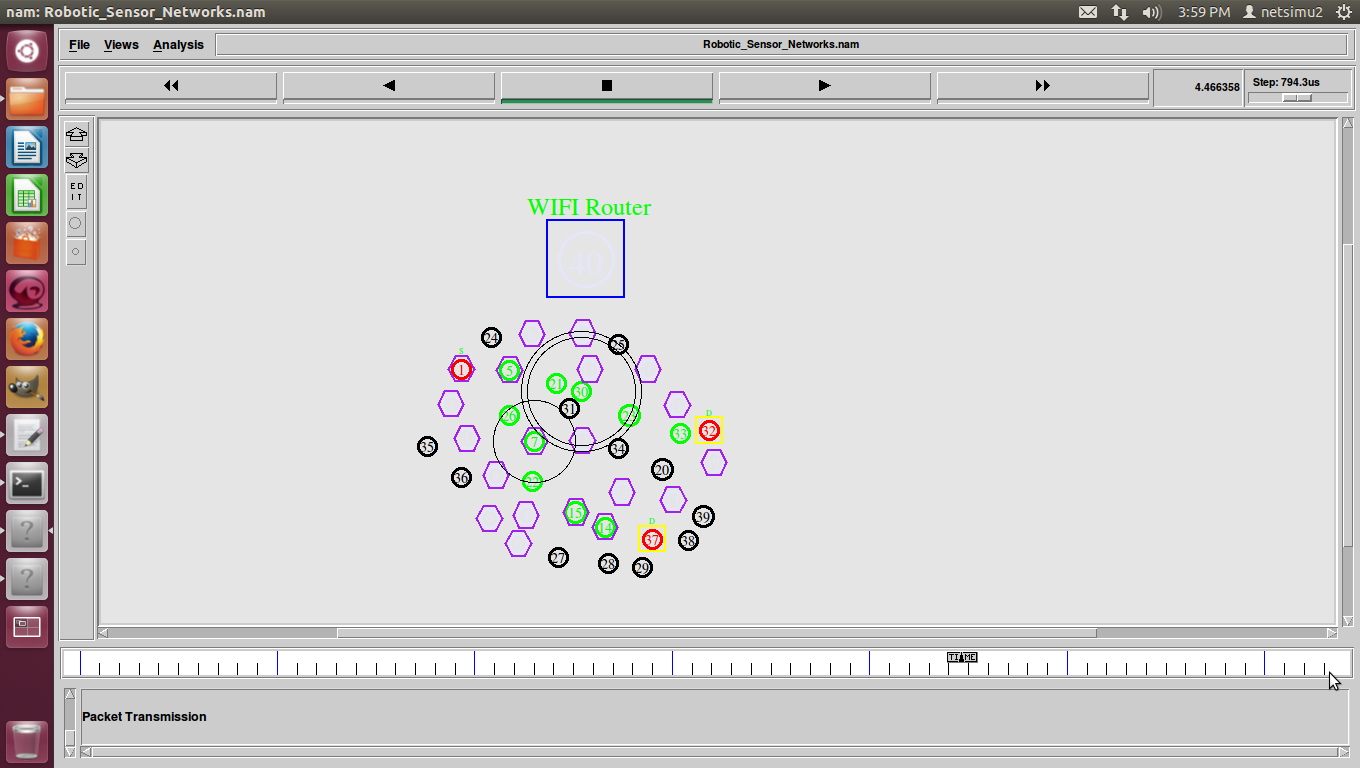
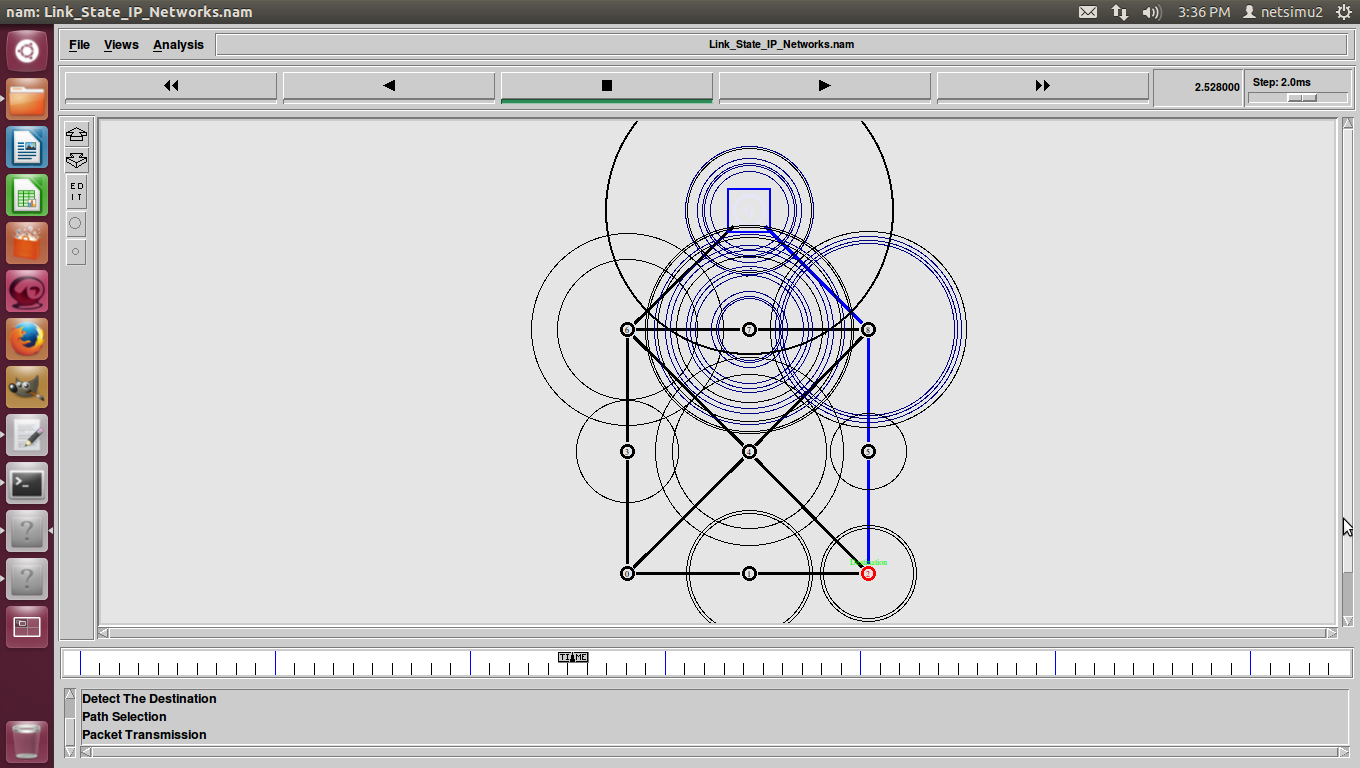
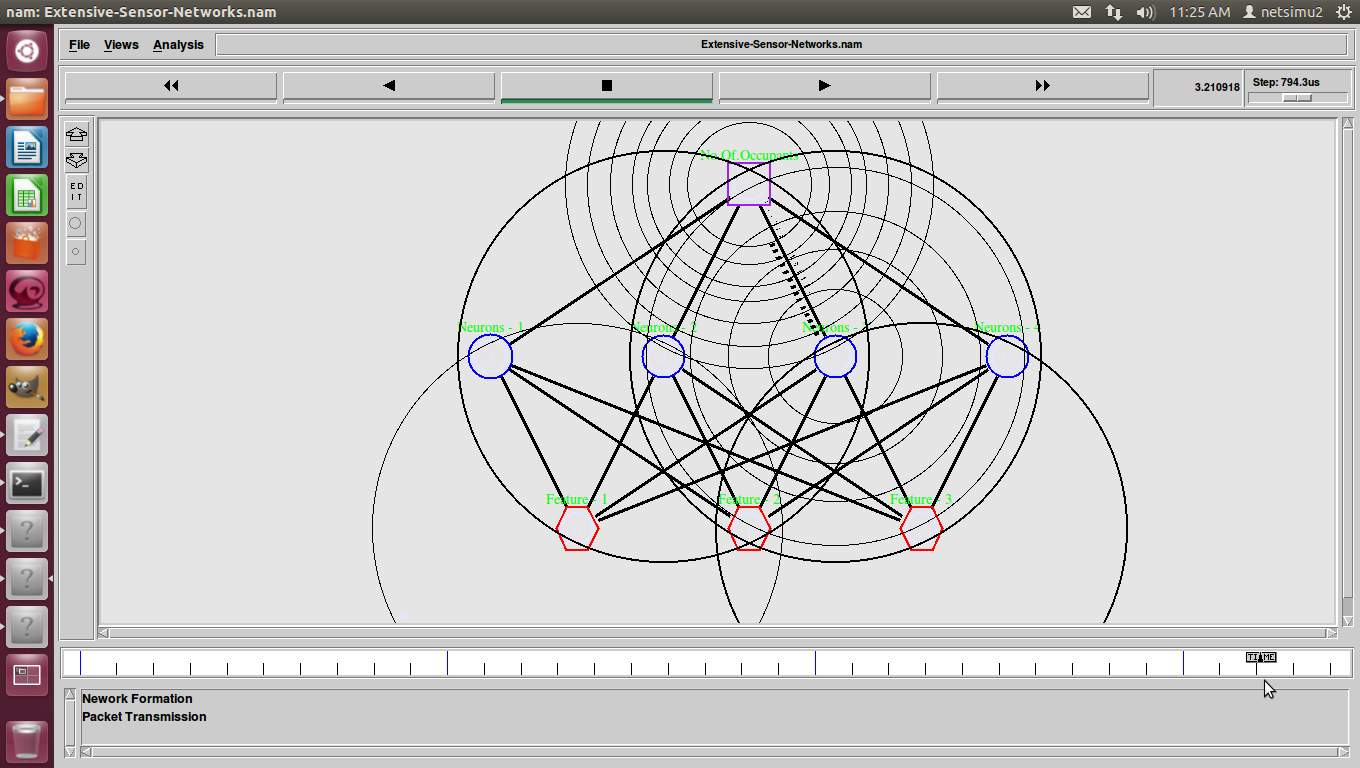
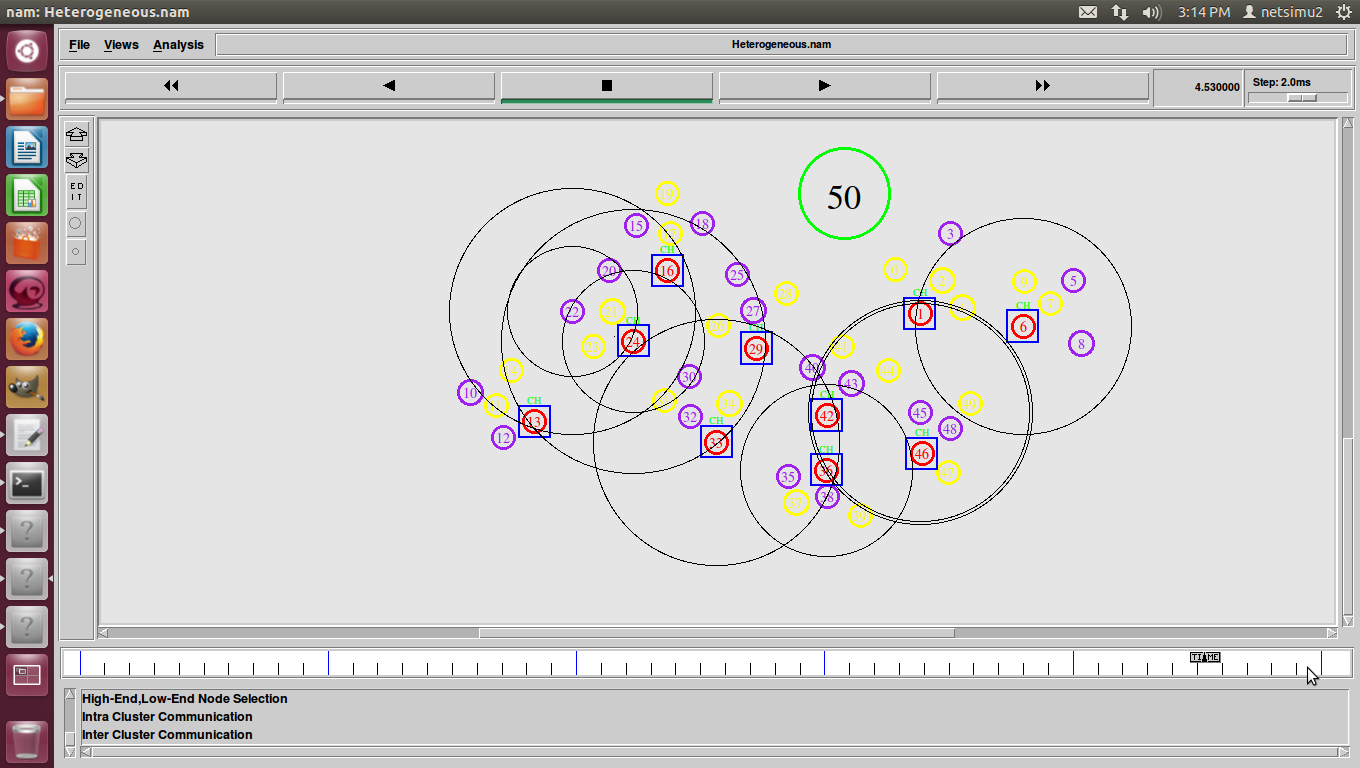
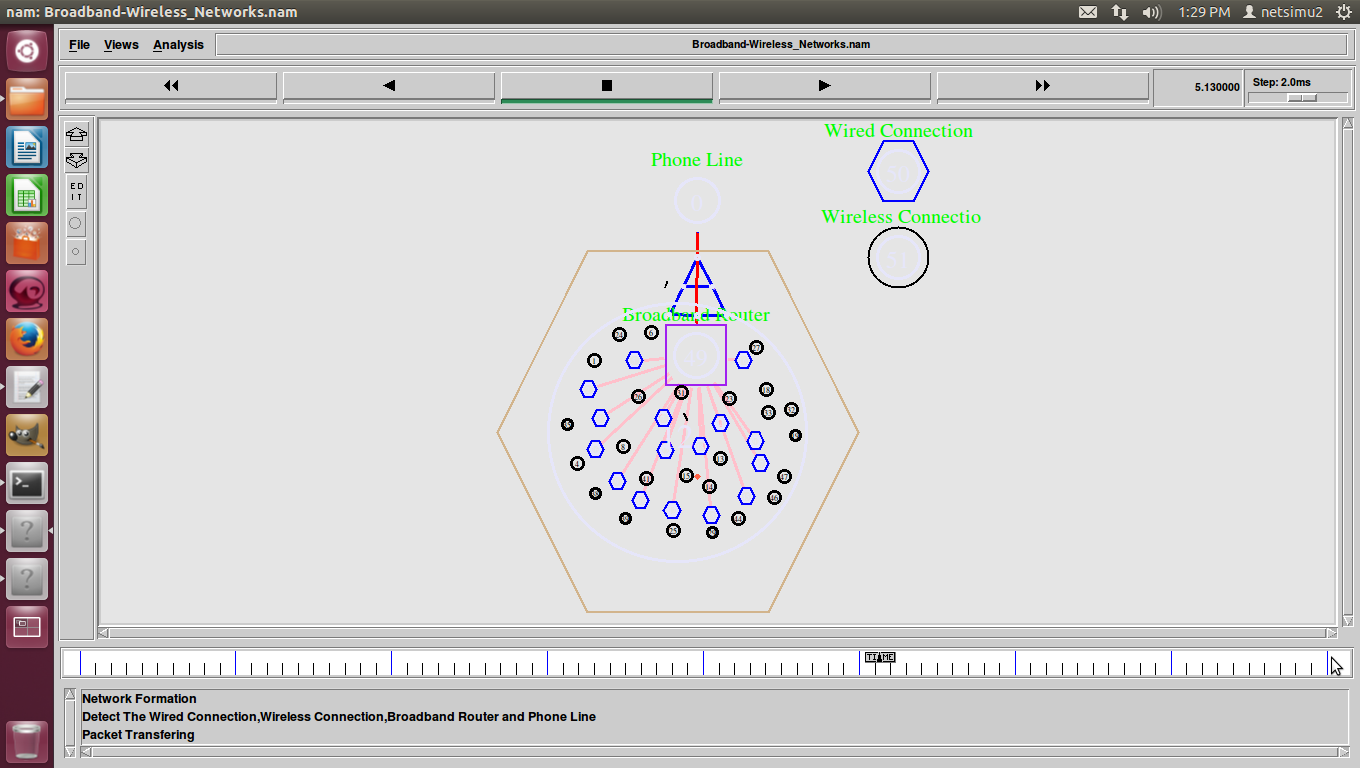
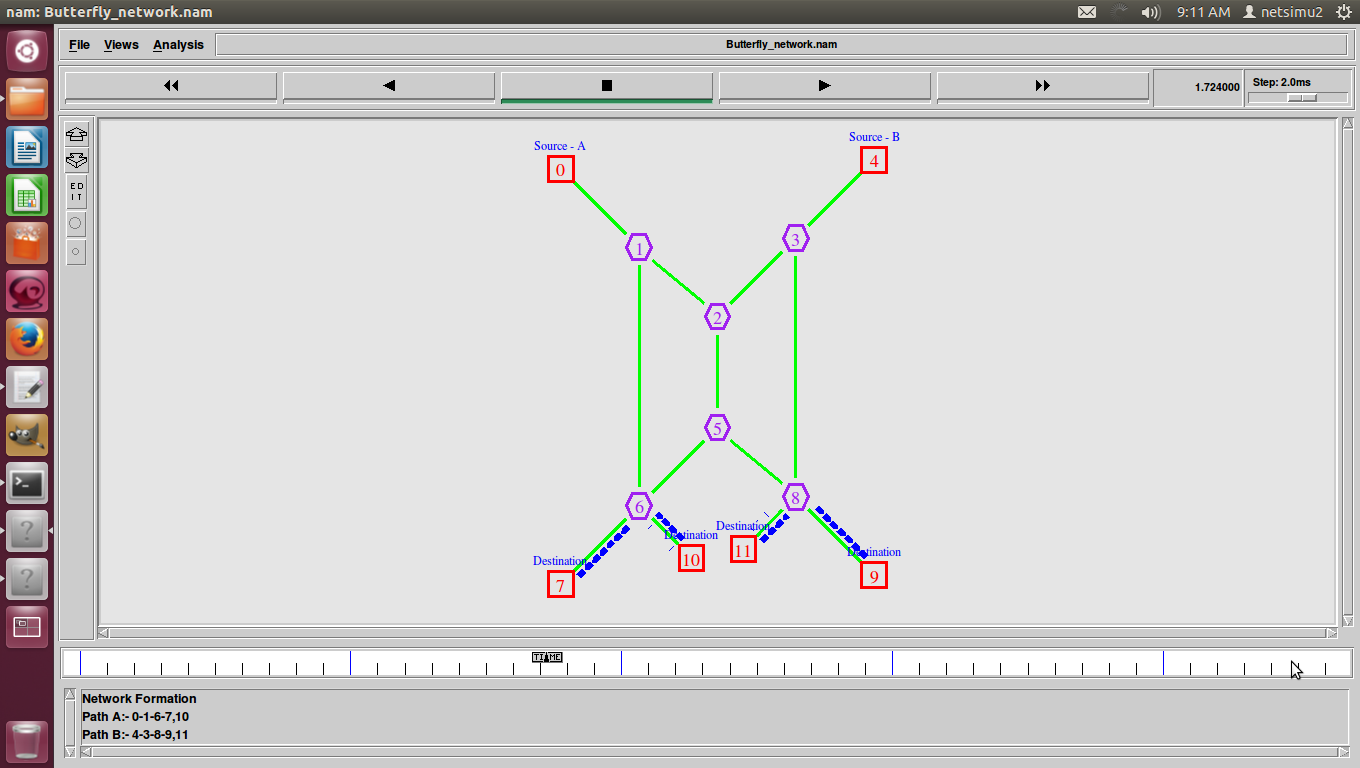
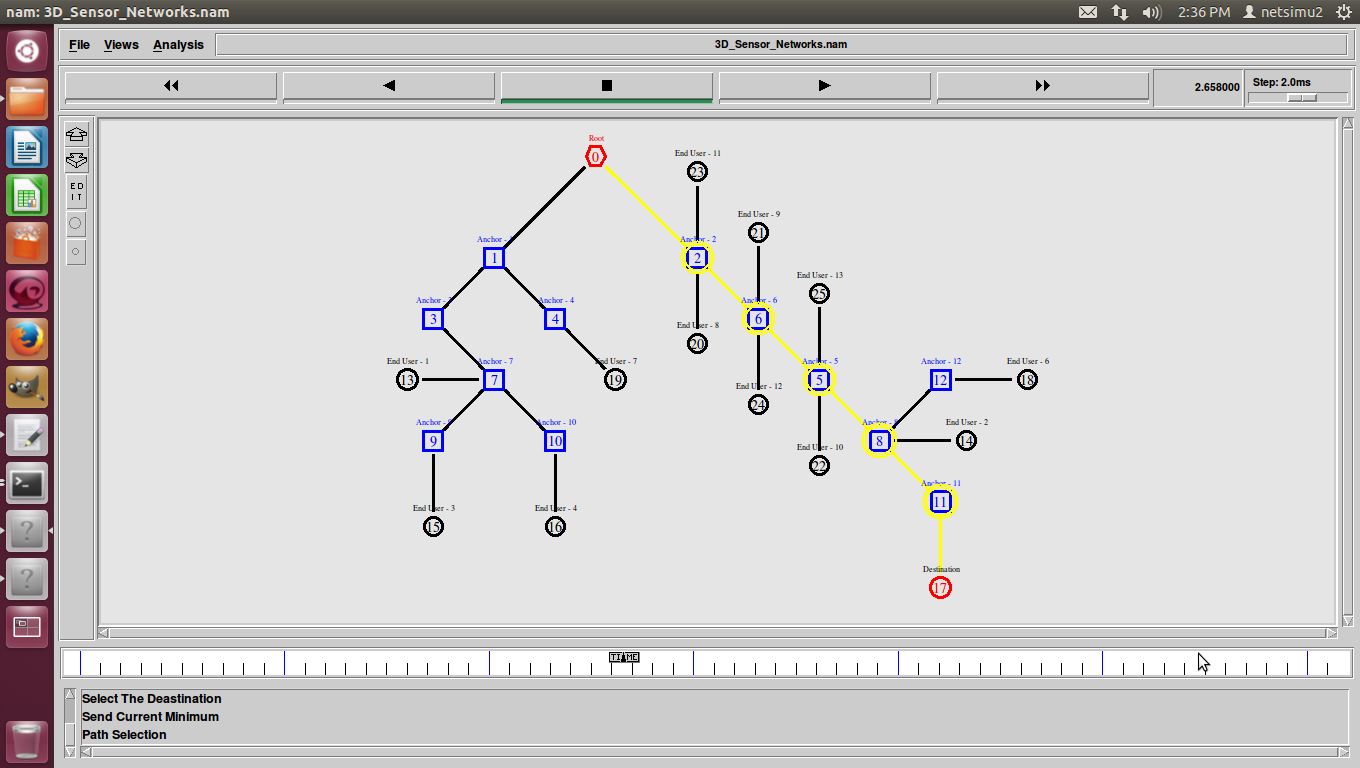
Shortest Path Routing in Ns2 also refers to the process of finding paths through a network also that have a minimum of distance or other cost metric.
What is shortest-path-routing?
- In general it could also a function of distance, bandwidth, average traffic, communication cost, mean queue length, and also measure delay, router processing speed, etc.
- Routing of data packets on the Internet is also an example involving millions of routers in a complex, worldwide, also in multilevel network. Optimum routing also on the Internet has a major impact on performance and cost.
Different ways to Identify shortest path-routing-in ns-2.
- Transmission and also propagation delays.
- Queuing delays.
- Minimum number of hops.
Key Algorithm used in Shortest-Path-routing in Ns-2
Sample code for Shortest Path Routing in Ns2.
void DSDV_Agent::tracepkt (Packet * p, double now, int me, const char *type)
{
char buf[1024];
unsigned char *walk = p->accessdata ();
int ct = *(walk++);
int seq, dst, met;
snprintf (buf, 1024, "V%s %.5f _%d_ [%d]:", type, now, me, ct);
while (ct--)
{
dst = *(walk++);
dst = dst << 8 | *(walk++);
dst = dst << 8 | *(walk++);
dst = dst << 8 | *(walk++);
met = *(walk++);
seq = *(walk++);
seq = seq << 8 | *(walk++);
seq = seq << 8 | *(walk++);
seq = seq << 8 | *(walk++);
snprintf (buf, 1024, "%s (%d,%d,%d)", buf, dst, met, seq);
}
// Now do trigger handling.
//trace("VTU %.5f %d", now, me);
if (verbose_)
trace ("%s", buf);
}
// Prints out an rtable element.
void
DSDV_Agent::output_rte(const char *prefix, rtable_ent * prte, DSDV_Agent * a)
{
a->trace("DFU: deimplemented");
printf("DFU: deimplemented");
prte = 0;
prefix = 0;
#if 0
printf ("%s%d %d %d %d %f %f %f %f 0x%08x\n",
prefix, prte->dst, prte->hop, prte->metric, prte->seqnum,
prte->udtime, prte->new_seqnum_at, prte->wst, prte->changed_at,
(unsigned int) prte->timeout_event);
a->trace ("VTE %.5f %d %d %d %d %f %f %f %f 0x%08x",
Scheduler::instance ().clock (), prte->dst, prte->hop, prte->metric,
prte->seqnum, prte->udtime, prte->new_seqnum_at, prte->wst, prte->changed_at,
prte->timeout_event);
#endif
}
Tweet